Novel Approaches for Developing New Antibiotics
Main Article Content
Abstract
Antibiotics are an essential part of modern medicine. The creation of antibiotic-resistant mutations among bacteria appears to be unavoidable, and after a few decades, the antibiotic's potency will be reduced, and the antibiotic will be phased out of general use.
The usual approach to dealing with this issue has been to release new antibiotics that kill resistant mutants.
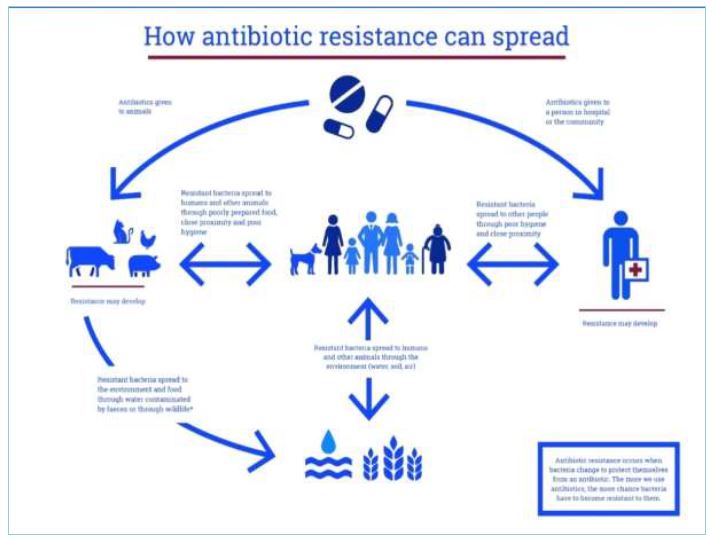
Antibiotics such as penicillin, erythromycin, and methicillin are used to treat infectious infections, however these antibiotics are becoming less efficient as bacteria develop more resistant to them.
Natural products are microorganism, plant, and animal metabolites.
These natural compounds have been used to make lead molecules, which have been used to make a variety of synthetic medications.
Actinomycetes can create a wide range of bioactive compounds, which have been used to treat a number of human infections. Teixobactin was discovered using a new method of culturing bacteria in soil from “a grassy field in Maine.” It is active against gram-positive bacteria this review article focuses on different sources of new antibiotics.
Bacteriophages have been found to be antibacterial in animals and could be useful in the treatment of some infectious disorders.
Another option is to develop new antibiotics that target non-multiplying bacteria, which could lead to medications that limit the emergence of antibiotic resistance and improve patient compliance by reducing antibiotic therapy duration.
With one exception, these new discovery techniques have resulted in medicines that are in preclinical research but have not yet entered clinical trials.
For the time being, the bulk of novel antibiotics on the market will most likely be structural mimics of existing antibiotic families or new compounds, both natural and non-natural, that are evaluated against live growing bacteria in the traditional fashion.